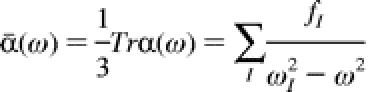-
Clusters of alkali and alkaline earth metals : a new synthetic approach, single crystal structures, theoretical calculations and potential applications
K.M. Fromm, E.D. Gueneau, G. Bernardinelli, H. Goesmann, J. Weber, M.J. Mayor-Lopez, P. Boulet and H. Chermette
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 125 (12) (2003), p3593-3604


DOI:10.1021/ja0205737 | unige:3684 | Abstract | Article HTML | Article PDF
A new synthetic approach, reacting alkaline earth metal iodides with butyllithium, lithium hydroxide, and/or lithium butoxide under salt elimination, is presented, giving access to some interesting clusters of calcium, strontium, and barium, partially in combination with lithium. The so far largest calcium cluster Li[{Ca7(őľ3-OH)8I6(thf)12}2(őľ2-I)]¬∑3THF, 4, and the new strontium compound [Sr3I3(OH)2(thf)9]I, 5, are shown to feature common building blocks of OH-capped M3 triangles. On the basis of mainly electrostatic interactions, these clusters are not volatile. By introducing LiOtBu, the two clusters [IM(OtBu)4{Li(thf)}4(OH)] (6, M = Sr; 7, M = Ba) are prepared, 7 exhibiting volatility as an important physical property, which makes it a potential precursor for chemical vapor deposition. The structural relationship between 4, 5, 6, and 7 and their respective starting materials is shown, and possible reaction mechanisms are proposed. Exhibiting surprising and new structural motifs, the bonding modes of these clusters are investigated by the electron localization function as well as by ab initio calculations.